RabbitMQ¶
Contents
Cluster start and stop¶
Stop¶
Ensure that any services using RabbitMQ are stopped.
Stop the rabbitmq container on all controller nodes (one by one) and note the order of the nodes.
docker stop rabbitmq
Start¶
Successively start the rabbitmq container on all controller nodes (one by one) in the reverse order.
docker start rabbitmq
Check¶
old RabbitMQ
docker exec -it rabbitmq rabbitmqctl cluster_status
Cluster status of node 'rabbit@testbed-node-1'
[{nodes,[{disc,['rabbit@testbed-node-0','rabbit@testbed-node-1']}]},
{running_nodes,['rabbit@testbed-node-0','rabbit@testbed-node-1']},
{cluster_name,<<"rabbit@testbed-node-0.osism.local">>},
{partitions,[]},
{alarms,[{'rabbit@testbed-node-0',[]},{'rabbit@testbed-node-1',[]}]}]
new RabbitMQ
docker exec -it rabbitmq rabbitmqctl cluster_status
Cluster status of node rabbit@node01 ...
Basics
Cluster name: rabbit@node03.osism.local
Disk Nodes
rabbit@node01
rabbit@node02
rabbit@node03
Running Nodes
rabbit@node01
rabbit@node02
rabbit@node03
Versions
rabbit@node01: RabbitMQ 3.8.16 on Erlang 23.3.3
rabbit@node02: RabbitMQ 3.8.16 on Erlang 23.3.3
rabbit@node03: RabbitMQ 3.8.16 on Erlang 23.3.3
Maintenance status
Node: rabbit@node01, status: not under maintenance
Node: rabbit@node02, status: not under maintenance
Node: rabbit@node03, status: not under maintenance
Alarms
(none)
Network Partitions
(none)
Listeners
Node: rabbit@node01, interface: [::], port: 15672, protocol: http, purpose: HTTP API
Node: rabbit@node01, interface: [::], port: 15692, protocol: http/prometheus, purpose: Prometheus exporter API over HTTP
Node: rabbit@node01, interface: [::], port: 25672, protocol: clustering, purpose: inter-node and CLI tool communication
Node: rabbit@node01, interface: 10.2.8.11, port: 5672, protocol: amqp, purpose: AMQP 0-9-1 and AMQP 1.0
Node: rabbit@node02, interface: [::], port: 15672, protocol: http, purpose: HTTP API
Node: rabbit@node02, interface: [::], port: 15692, protocol: http/prometheus, purpose: Prometheus exporter API over HTTP
Node: rabbit@node02, interface: [::], port: 25672, protocol: clustering, purpose: inter-node and CLI tool communication
Node: rabbit@node02, interface: 10.2.8.12, port: 5672, protocol: amqp, purpose: AMQP 0-9-1 and AMQP 1.0
Node: rabbit@node03, interface: [::], port: 15672, protocol: http, purpose: HTTP API
Node: rabbit@node03, interface: [::], port: 15692, protocol: http/prometheus, purpose: Prometheus exporter API over HTTP
Node: rabbit@node03, interface: [::], port: 25672, protocol: clustering, purpose: inter-node and CLI tool communication
Node: rabbit@node03, interface: 10.2.8.13, port: 5672, protocol: amqp, purpose: AMQP 0-9-1 and AMQP 1.0
Feature flags
Flag: drop_unroutable_metric, state: enabled
Flag: empty_basic_get_metric, state: enabled
Flag: implicit_default_bindings, state: enabled
Flag: maintenance_mode_status, state: enabled
Flag: quorum_queue, state: enabled
Flag: user_limits, state: enabled
Flag: virtual_host_metadata, state: enabled
Emptying the notification queues¶
If notifications of individual services are activated and these notifications are not consumed, for example by Panko, over the course of time many unprocessed messages accumulate on the individual notification queues.
docker exec -it rabbitmq rabbitmqctl list_queues | grep -v $'\t0'
Listing queues
versioned_notifications.info 2983
versioned_notifications.error 29
docker exec -it rabbitmq rabbitmqctl purge_queue versioned_notifications.info
Purging queue 'versioned_notifications.info' in vhost '/'
rabbitmqadmin¶
https://www.rabbitmq.com/management-cli.html
The management plugin ships with a command line tool rabbitmqadmin which can perform some of the same actions as the Web-based UI, and which may be more convenient for automation tasks. Note that rabbitmqadmin is just a specialised HTTP client; if you are contemplating invoking rabbitmqadmin from your own program you may want to consider using an HTTP API client library instead.
curl -o rabbitmqadmin http://api-int.osism.local:15672/cli/rabbitmqadmin
Cluster status¶
old RabbitMQ
docker exec -it rabbitmq rabbitmqctl eval 'rabbit_clusterer:status().'
Rabbit is running in cluster configuration:
[{node_ids,[{'rabbit@testbed-node-0',<<33,223,136,84,52,55,149,250,118,202,
103,22,88,214,60,236>>},
{'rabbit@testbed-node-1',<<186,47,70,175,150,251,92,174,244,196,
192,37,25,113,247,124>>}]},
{gospel,{node,'rabbit@testbed-node-0'}},
{nodes,[{'rabbit@testbed-node-0',disc},{'rabbit@testbed-node-1',disc}]},
{version,1}]
Running nodes: ['rabbit@testbed-node-0','rabbit@testbed-node-1']
ok
new RabbitMQ
docker exec -it rabbitmq rabbitmqctl cluster_status
Cluster status of node rabbit@node01 ...
Basics
Cluster name: rabbit@node03.osism.local
Disk Nodes
rabbit@node01
rabbit@node02
rabbit@node03
Running Nodes
rabbit@node01
rabbit@node02
rabbit@node03
Versions
rabbit@node01: RabbitMQ 3.8.16 on Erlang 23.3.3
rabbit@node02: RabbitMQ 3.8.16 on Erlang 23.3.3
rabbit@node03: RabbitMQ 3.8.16 on Erlang 23.3.3
Maintenance status
Node: rabbit@node01, status: not under maintenance
Node: rabbit@node02, status: not under maintenance
Node: rabbit@node03, status: not under maintenance
Alarms
(none)
Network Partitions
(none)
Listeners
Node: rabbit@node01, interface: [::], port: 15672, protocol: http, purpose: HTTP API
Node: rabbit@node01, interface: [::], port: 15692, protocol: http/prometheus, purpose: Prometheus exporter API over HTTP
Node: rabbit@node01, interface: [::], port: 25672, protocol: clustering, purpose: inter-node and CLI tool communication
Node: rabbit@node01, interface: 10.2.8.11, port: 5672, protocol: amqp, purpose: AMQP 0-9-1 and AMQP 1.0
Node: rabbit@node02, interface: [::], port: 15672, protocol: http, purpose: HTTP API
Node: rabbit@node02, interface: [::], port: 15692, protocol: http/prometheus, purpose: Prometheus exporter API over HTTP
Node: rabbit@node02, interface: [::], port: 25672, protocol: clustering, purpose: inter-node and CLI tool communication
Node: rabbit@node02, interface: 10.2.8.12, port: 5672, protocol: amqp, purpose: AMQP 0-9-1 and AMQP 1.0
Node: rabbit@node03, interface: [::], port: 15672, protocol: http, purpose: HTTP API
Node: rabbit@node03, interface: [::], port: 15692, protocol: http/prometheus, purpose: Prometheus exporter API over HTTP
Node: rabbit@node03, interface: [::], port: 25672, protocol: clustering, purpose: inter-node and CLI tool communication
Node: rabbit@node03, interface: 10.2.8.13, port: 5672, protocol: amqp, purpose: AMQP 0-9-1 and AMQP 1.0
Feature flags
Flag: drop_unroutable_metric, state: enabled
Flag: empty_basic_get_metric, state: enabled
Flag: implicit_default_bindings, state: enabled
Flag: maintenance_mode_status, state: enabled
Flag: quorum_queue, state: enabled
Flag: user_limits, state: enabled
Flag: virtual_host_metadata, state: enabled
Broken queue¶
2020-03-20 17:24:44.846 6 ERROR oslo_service.service MessageDeliveryFailure: Unable to connect to AMQP server on 10.49.20.11:5672 after None tries: Queue.declare: (404) NOT_FOUND - failed to perform operation on queue 'dhcp_agent.30-02' in vhost '/' due to timeout
Stop the service, delete the queue and start the service.
Set number of Erlang schedulers¶
Schedulers in the runtime assign work to kernel threads that perform it. By default the runtime will start one scheduler for one CPU core it detects. This can lead to permanent high CPU utilisation. Setting the number of schedulers to a lower value, will decrease CPU utilisation considerably.
environments/kolla/configuration.yml
rabbitmq_server_additional_erl_args: "+S 1:1"
See RabbitMQ documentation for more details.
Unsynchronized queues¶
Due to server crashes or rabbitmq container restarts there might be unsynchronized queues. To verify this open the web console for RabbitMQ via https://api-int.osism.local:15672 and switch to the Queues tab. In the nodes column you see the master node for that queue as well as the number of synchronized (and if the case in red) the unsynchronized mirrors for that queue. If you happen to have unsynchronized queues, click on the queue and you should see a button to force synchronization. After that you should see the same number of synchronized mirrors for all queues.
To check via CLI you can use this command and check that slave_pids and
synchronized_slave_pids are identical and also contain cluster_size - 1
number of entries.
docker exec -it rabbitmq rabbitmqctl list_queues name policy slave_pids synchronised_slave_pids
Queues missing mirrors¶
From time to time (especially after provisioning new RabbitMQ nodes or after
reboots of RabbitMQ nodes) that the number of synchronized mirrors matches the
number of RabbitMQ nodes in your cluster. To do so, check the RabbitMQ web
console at https://api-int.osism.local:15672 in the queues tab. The number
of synchronized mirror (blue icon with a +<number>) should match the number of
RabbitMQ nodes minus one (the master for that queue). So on a three node
RabbitMQ cluster there should be a +2 icon for each queue.
How to fix missing mirrors¶
If you miss a mirror (so in the above example, if you only see a +1 on certain queues) there is a workaround possible to restore the missing mirrors.
Create a new ha-all policy with a priority of 1 and assign it to all
queues. That should add the missing mirrored queues. After that you can remove
the policy again and the queues fall back to their default ha-all policy.
The screenshot shows the settings on how to do this via the web console.
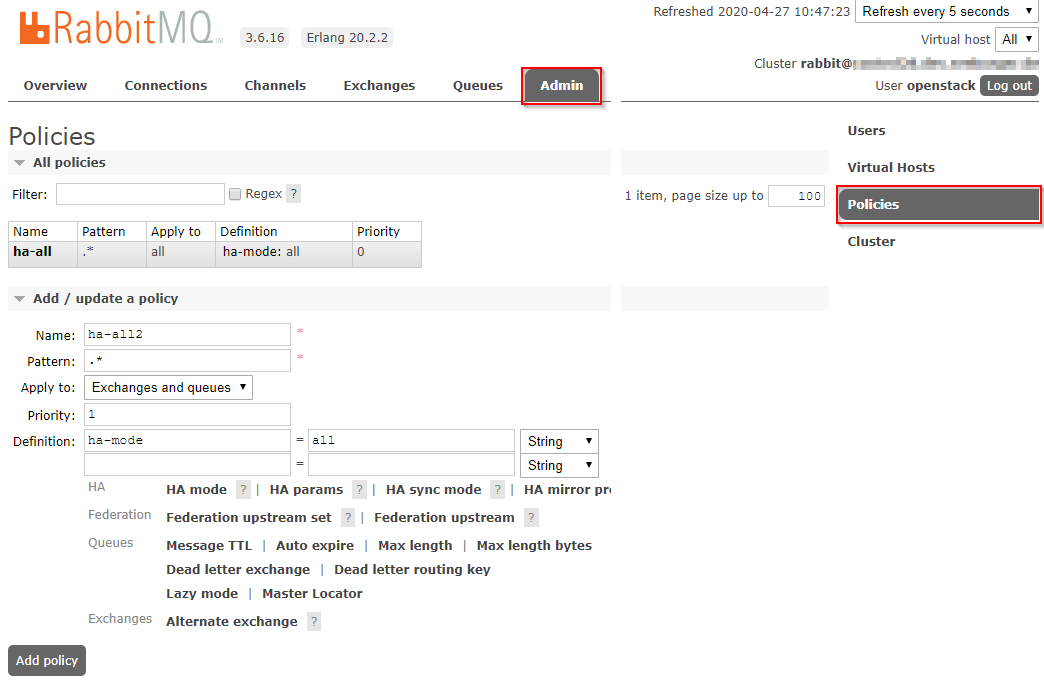
Parameter |
Value |
Name |
ha-all2 |
Pattern |
.* |
Priority |
1 |
ha-mode |
all |
Set rabbitmq extra config (>=Yoga)¶
To set other option in RabbitMQ, you can use the rabbitmq_extra_config variable. It’s only for same or higher release than yoga. For example, to set heartbed option:
environments/kolla/configuration.yml
rabbitmq_extra_config:
heartbeat: 640
ssl_handshake_timeout: 20000
handshake_timeout: 40000